An Overview of EHS Compliance, Standards, and Regulations
EHS compliance isn’t just a checkbox — it’s how organizations keep people safe, protect the planet, and avoid costly legal trouble. From reducing workplace accidents to staying on the right side of regulators, a strong EHS program is critical for both reputation and results.
The following is a brief overview of EHS guidelines, standards, and regulations, along with guidance on how to remain compliant.
What is EHS compliance?
EHS compliance means following the environmental, health, and safety laws and standards that apply to your business. It’s the legal side of your EHS program — making sure you're meeting the rules that protect workers, communities, and the environment.
Compliance is a core part of EHS management. While EHS management covers your entire strategy for preventing harm, EHS compliance focuses on what’s required by law — from providing PPE to properly storing hazardous waste.

EHS rules are enforced by a mix of government agencies — depending on where you operate and what you do. In the U.S., some of the key regulators include OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), and local/state agencies which may enforce additional rules, issue permits, and conduct inspections based on regional laws.
Failing to comply can lead to penalties and shutdowns on the legal side, as well as loss of life and damage to your physical assets and the environment. Rules can seem too strict and overbearing, but they are there for a reason.
General EHS guidelines that every organization should follow
While specific regulations vary by industry and region, there are several foundational guidelines that apply to virtually all organizations. Below is a quick look at the general best practices that should shape your EHS programs.

Environmental guidelines
Environmental protection is a key responsibility for any organization. These guidelines focus on minimizing harm to the natural environment:
- Pollution prevention: Taking steps to reduce emissions to air, water, and soil through cleaner processes and proper containment.
- Waste management: Handling, storing, and disposing of all waste — especially hazardous materials — in accordance with regulations.
- Resource efficiency: Conserving energy, water, and raw materials through sustainable practices.
- Environmental compliance: Securing and maintaining all required environmental permits and ensuring day-to-day operations meet legal requirements.
- Emergency preparedness: Developing clear plans to respond to environmental incidents like chemical spills or leaks.
Health guidelines
Protecting employee health goes beyond avoiding accidents — it means reducing exposure to harmful conditions and promoting overall wellness:
- Exposure controls: Identifying and limiting risks from chemicals, noise, dust, or biological agents.
- Hygiene and sanitation: Providing clean facilities, including restrooms, washing stations, and first aid supplies.
- Health monitoring: In high-risk environments, conducting periodic checks, such as hearing tests or respiratory exams.
- Mental health support: Encouraging open communication, stress management, and access to support resources.
- Disease prevention: Where relevant, implementing vaccinations or infection control measures.
Safety guidelines
Workplace safety is about actively preventing injuries and accidents. These core safety practices apply across all sectors:
- Hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA): Regularly evaluating the work environment for potential dangers.
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE): Ensuring employees are equipped with — and trained on — proper safety gear.
- Equipment safety: Training staff on safe equipment use and implementing controls like lockout/tagout procedures.
- Safe work practices: Developing clear rules for high-risk tasks such as working at heights or in confined spaces.
- Incident reporting: Establishing a consistent process for logging, investigating, and learning from incidents or near misses.
Common EHS standards and regulations
EHS regulations come from a mix of federal, international, and industry-specific sources. While the exact requirements vary depending on your sector and location, there are several key standards that every organization should be aware of:
- OSHA: In the U.S., OSHA sets and enforces standards for workplace safety and health. Common requirements include hazard communication, fall protection, machine guarding, and mandatory training. OSHA also requires incident reporting and recordkeeping for workplace injuries.
- EPA: The EPA regulates activities that impact the environment — like air and water emissions, chemical storage, and waste disposal. Depending on your operations, you may need specific permits and regular monitoring to stay compliant.
- ISO 14001: It is an international standard that helps organizations manage their environmental responsibilities. It’s not legally required, but it provides a proven framework for identifying environmental risks, improving performance, and staying compliant with local laws.
As we mentioned earlier, some industries have their own sets of rules — often more detailed or demanding than general regulations. For example:
- Construction must follow strict fall protection, scaffolding, and excavation standards.
- Manufacturers might face additional rules around machine safety, chemical exposure, and noise levels.
- Laboratories must manage chemical hygiene, biosafety protocols, and the handling of hazardous materials.
The goal is to create safer, more sustainable operations that are built to last.
The path to EHS compliance
Staying compliant is all about following a clear process — from understanding what rules apply to your business to building systems that keep you on the right track.
Whether you're starting from scratch or tightening up your current program, the steps below will help you build a strong foundation.
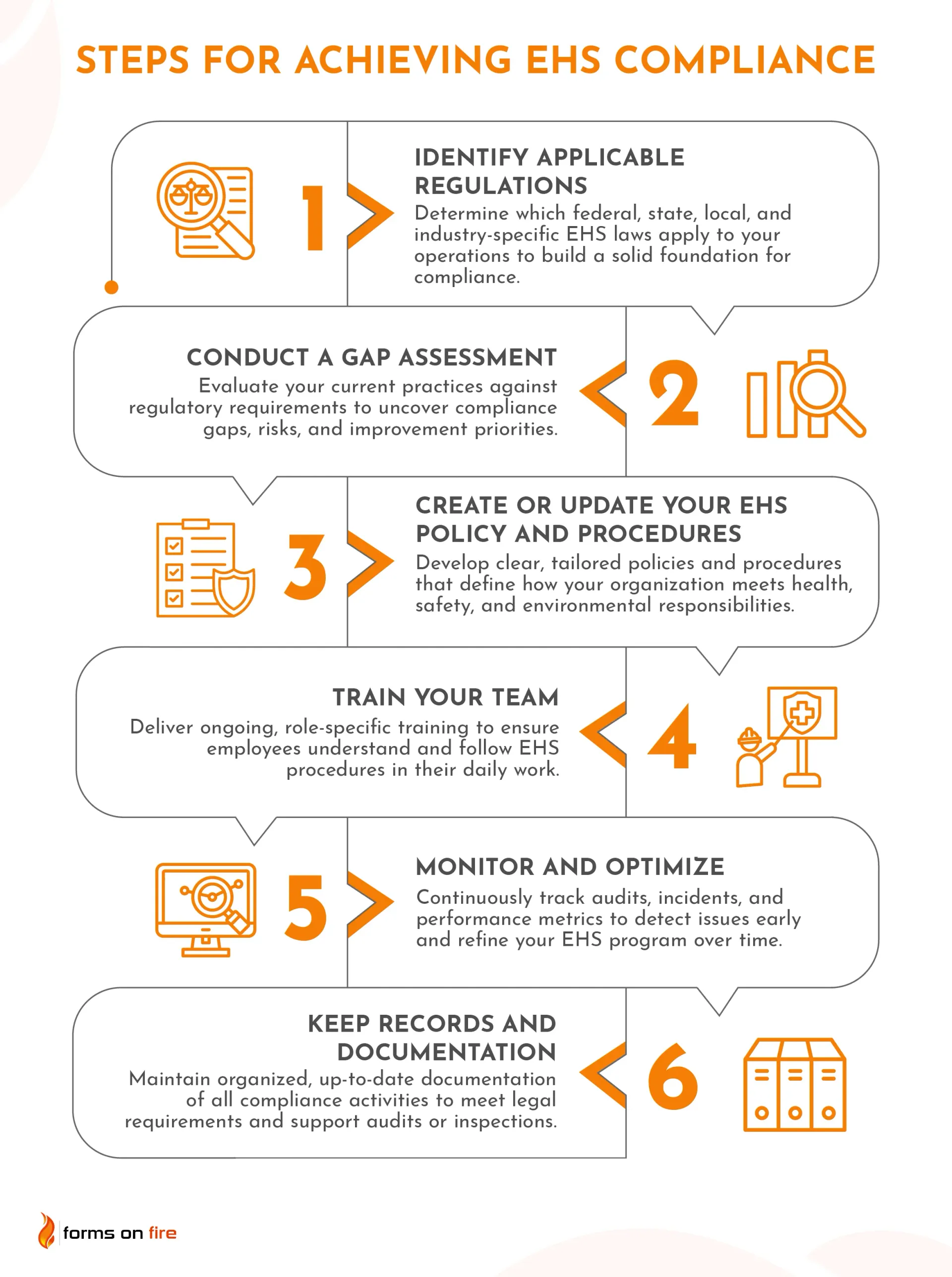
Step 1: Identify applicable regulations
The first step in EHS compliance is figuring out exactly which laws, standards, and regulations apply to your business. This may sound obvious, but it's where many organizations go wrong — either by assuming general rules cover everything or by missing specific industry-specific requirements.
To get this right:
- Review federal regulations like OSHA and EPA rules.
- Look into ISO standards if you’re aiming for international or certification-level compliance.
- Don’t overlook federal, state, and local EHS laws or permit requirements.
- Check for industry-specific standards (e.g., construction, manufacturing, healthcare) tied to your sector.
- Consider the type of operations you are running — working with chemicals, operating heavy equipment, emitting pollutants, etc. — as these will come with specific guidelines to follow.
Think of this as your compliance foundation. You can’t build a solid EHS program if you don’t know what you're trying to comply with.
🔍 Tip: Keep a master list of all applicable requirements — and update it when your operations or regulations change.
Step 2: Conduct a gap assessment
Once you know what regulations apply, the next step is to see how your current practices stack up. This is where a gap assessment comes in — a structured way to compare what you’re doing now against what you’re supposed to be doing.
A good gap assessment will help you spot missing or outdated policies, identify risks and weaknesses in your current EHS program, and prioritize what needs to be fixed or improved.
There are a few ways to approach it:
- Use digital checklists to evaluate processes and documents.
- Perform internal audits using your compliance requirements as benchmarks.
- Bring in a third-party consultant for a fresh set of eyes.
The goal here isn’t to point fingers — it’s to find issues before they turn into violations or incidents. Think of it as your compliance health check.
✅ Tip: Document everything during the assessment. You’ll need this info to guide updates and track progress.
Step 3: Create or update your EHS policy and procedures
Now that you’ve identified the gaps, it’s time to put (or update) your EHS policy and procedures in writing. These documents are the backbone of your compliance program — they show how your organization plans to meet its legal and safety obligations, day to day.
A solid EHS policy should clearly outline your company’s commitment to health, safety, and environmental protection. From there, your procedures explain how that commitment is put into action.
Your documentation should cover core areas like:
- Workplace inspections and safety audits
- Hazard identification and control measures
- Emergency preparedness and response
- Incident reporting and investigation
- Roles and responsibilities for compliance tasks.
Keep it simple, accessible, and specific to your operations. Avoid generic copy-paste templates — tailor your policies so your team knows exactly what to do and who’s responsible for what.
🔄 Tip: Review and update these documents regularly, especially after incidents, audits, or regulatory changes.
Step 4: Train your team
Everything you’ve done up to this point will mean little if your frontline team doesn’t understand your EHS policy or doesn’t know how to apply it. Training is what turns your compliance plans into everyday practice.
Make sure your training covers:
- Safety protocols for daily tasks and high-risk activities.
- Hazard recognition — how to spot and report risks.
- PPE — what to wear, when, and how to use it correctly.
- Emergency response procedures.
- Incident reporting and what to do after an event or near miss.
Good training is role-specific (different jobs face different risks), ongoing (not just once during onboarding), and accessible (think mobile learning or short, digestible modules).
🎯 Tip: Mix in interactive or digital formats — quizzes, videos, role-playing different scenarios — to boost engagement and retention. It’s how you make compliance easy.
Step 5: Monitor and optimize
EHS compliance isn’t “set it and forget it.” It’s an ongoing process — and staying compliant means keeping an eye on how your program is performing over time. Regular monitoring enables you to identify issues early, stay ahead of regulatory changes, and continually improve your procedures.
What to track:
- Inspections and audits: Routine checks help verify compliance and spot gaps.
- Incident logs: Analyze what went wrong — or nearly went wrong — to prevent repeat issues.
- Safety KPIs: Track metrics like near misses, lost-time incidents, Total Recordable Incident Rate, or training completion rates.
Look for patterns, take corrective action, and adjust your policies as needed. Your EHS program should evolve as your operations — and the risks you face — change.
🔄 Tip: Use findings from audits or incident reporting forms to drive real improvements, not just check boxes.
Step 6: Keep records and documentation
If it’s not documented, it didn’t happen — at least in the eyes of regulators. Good recordkeeping is both a legal requirement and a powerful tool for managing your EHS program.
You should maintain clear, organized records for:
- Training sessions and attendance
- Inspections and audit results
- Incident and near-miss reports
- Corrective actions taken
- Permits, certifications, and compliance reports
Solid documentation will help prove compliance during inspections or audits, spot trends and recurring issues, and make data-driven decisions about safety and environmental performance.
As with almost everything, digital tools can make this whole process a whole lot easier:
- Secure cloud storage keeps everything in one place and accessible to authorized users.
- Searchable databases and automatic reports speed up reporting and data retrieval.
- Historical data helps you see what’s improving — and what’s not.
🗂️ Tip #1: Standardize your file naming and folder structure so documents are easy to find, especially during audits.
🛠️ Tip #2: Use digital forms with automatic time stamps and user IDs to strengthen accountability and reduce manual errors.
How digital tools like Forms On Fire can simplify EHS compliance
Managing EHS compliance with paper forms, spreadsheets, or scattered systems is a recipe for frustration — and increased risk. Manual processes lead to missed inspections, lost reports, delayed responses, and siloed data that’s hard to act on.
That’s where tools like Forms On Fire come in.
Forms On Fire is an award-winning no-code platform that EHS professionals use to create custom forms and apps to digitize and centralize EHS management. It makes compliance easier, faster, and more reliable with:
- Pre-built EHS form templates: Deploy ready-to-use forms for inspections, audits, incident reports, and more — or fully customize them to your workflow.
- Mobile data collection: Let field teams capture photos, fill out forms, and report issues instantly, even without internet access.
- Workflow automation: Automatically route reports to the right people, assign tasks, and set reminders to keep things moving.
- Real-time reporting and dashboards: Monitor trends, safety metrics, and compliance status in one central dashboard. Automatically generate and send reports to different stakeholders.
- Centralized documentation: Store all EHS records securely in the cloud, making them easy to access, search, and share when needed.
Case study
M&S Food Industries improved their EHS compliance and reduced response times by switching to Forms On Fire. With custom mobile forms and real-time workflows, they streamlined reporting, improved team accountability, and made better use of their safety data.
Ready to make EHS compliance easier and more efficient?
👉 Book a demo with Forms On Fire and see how it can transform your EHS program.




