Using Technology to Streamline Operational Risk Management (ORM)
It's Monday morning. Your biggest client presentation is in two hours, and your entire system just crashed. Or maybe your star employee walked out the door with half your client relationships in their head. Sound familiar?
Welcome to operational risk — the universe's way of testing just how bulletproof your business really is.
While you can't prevent every curveball, you absolutely can change how you see them coming and what you do about them. Instead of just surviving the challenges, the smartest companies are using technology to turn operational risk management from a boring compliance exercise into their secret competitive weapon.
Want to know how? Let's pull back the curtain.
The main types of operational risk
Operational risk refers to the potential for loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events. Unlike credit risk or market risk, operational risk lurks in the day-to-day mechanics of how your organization actually runs.
Think of it as everything that can go wrong when you're trying to execute your business strategy. A system crashes during peak trading hours, a key employee walks out with sensitive data, or a hurricane shuts down your primary data center. These are the friction and failures that happen when real people use real systems to get work done.
Operational risk is divided into four main categories, and each one reflects different points where things can go wrong:
- Process risk: Breakdowns in workflows and procedures, like settlements following outdated procedures, or missing documentation for a safety procedure.
- People risk: Human errors and misconduct, including accidental data deletion, employee fraud, inadequate training, and situations where only one person knows a critical process.
- Technology risk: System failures and cyber threats, such as outages during peak hours, data breaches, legacy systems that can't integrate, and software bugs producing incorrect calculations.
- External event risk: Outside forces beyond your control, like natural disasters, sudden regulatory changes, supplier failures, and geopolitical events disrupting operations.
What makes operational risk particularly challenging is how these categories interconnect. A cyberattack (external event) might exploit weak password policies (process) implemented by undertrained staff (people) on vulnerable systems (technology). To build an effective defense, you must understand such interconnections.
Operational risk management framework
Operational risk management (ORM) is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring the risks that arise from operating in a particular environment.
The field has come a long way from the days of crossing fingers and hoping nothing goes wrong. Financial crises and corporate scandals forced organizations to get serious about operational risk — what used to be reactive firefighting is now proactive risk intelligence that actually informs business decisions.
Effective ORM integrates people, processes, and tools — ideally aligning with broader governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) strategies.

1. Identifying risks
Risk identification is the foundation of any operational risk management program. The principle is simple but critical: if you can't see the risk, you can't manage it.
There are numerous tools and methods for identifying risks:
- Risk assessments: Systematic evaluations of specific processes, departments, or activities.
- Internal and external audits: Regular reviews, such as operational audits or workplace safety audits, can help uncover non-obvious risks.
- Risk registers: Centralized databases tracking known risks across the organization.
- SWOT analysis: Examining strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Can be done at the level of the organization, department, or even a process.
- PESTLE analysis: Includes reviewing political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that impact your business.
- Employee surveys: Gathering insights from staff who see day-to-day operational challenges.
- Whistleblower reports: Anonymous channels for reporting misconduct or process failures.
- Incident analysis: Learning from past failures and near-misses.
- Scenario planning: Imagining potential future disruptions and their impacts.
To effectively identify risks, involve frontline staff who understand operational realities and utilize technology to detect concerning patterns and trends. Treat risk identification as a continual process, not just an annual task. Maintain multiple touchpoints throughout the year, foster ongoing reporting, and regularly reassess risks as operational conditions evolve.
2. Assessing risks
Once risks are identified, the next crucial step is determining their likelihood and impact. This assessment process transforms a long list of potential risks into a manageable, prioritized action plan by answering the fundamental question: which risks deserve immediate attention?
Common assessment methods include:
- Risk matrices: Simple likelihood x impact grids that plot risks on a visual scale from low to high probability and consequence.
- Monte Carlo simulations: Statistical modeling that runs thousands of scenarios to predict probability distributions of potential outcomes.
- Scenario analysis: Detailed exploration of specific "what-if" situations to understand potential impacts under different conditions.
- Other techniques: Bow-tie analysis for visualizing causes and consequences, fault tree analysis for systematic failure examination, and FMEA for structured process failure assessment.

Technology has changed how organizations assess risks. Digital forms help you automate data collection and scoring, eliminating manual spreadsheets and reducing human error. Visualization tools create intuitive heat maps and dashboards, making complex risk landscapes easy to understand. Predictive analytics uses historical data for more accurate probability estimates than traditional expert judgment alone.
Tip #1: Assessments must align with the organizational risk appetite. Labeling something "high risk" is pointless if leadership is not ready to support necessary changes.
Tip #2: Consistency across departments is important. Standardize your criteria to prevent different teams from giving wildly different ratings for the same risk.
3. Mitigating risks
Risk mitigation involves reducing either the likelihood or impact of identified risks through strategic controls and planning. The goal isn't to eliminate all risk — that's neither possible nor desirable — but to bring risks within acceptable tolerance levels while maintaining operational effectiveness.
Organizations typically deploy three types of mitigation strategies:
- Preventative controls: Stop risks from occurring in the first place through employee training programs, standard operating procedures (SOPs), access controls and authorization limits, segregation of duties, and robust hiring and background check processes.
- Detective controls: Identify risks or incidents as they happen through regular internal audits, real-time monitoring systems and alerts, transaction reviews and reconciliations, performance dashboards, and exception reporting mechanisms.
- Corrective controls: Minimize damage once a risk event occurs through disaster recovery and business continuity plans, incident response procedures, backup systems, data recovery processes, crisis communication protocols, and remediation workflows.
The T-A-A-M framework provides a structured approach to ease decision-making. Transfer shifts risk through insurance or outsourcing, Avoid eliminates unacceptable activities, Accept monitors risks within tolerance, and Mitigate applies controls to reduce likelihood or impact.
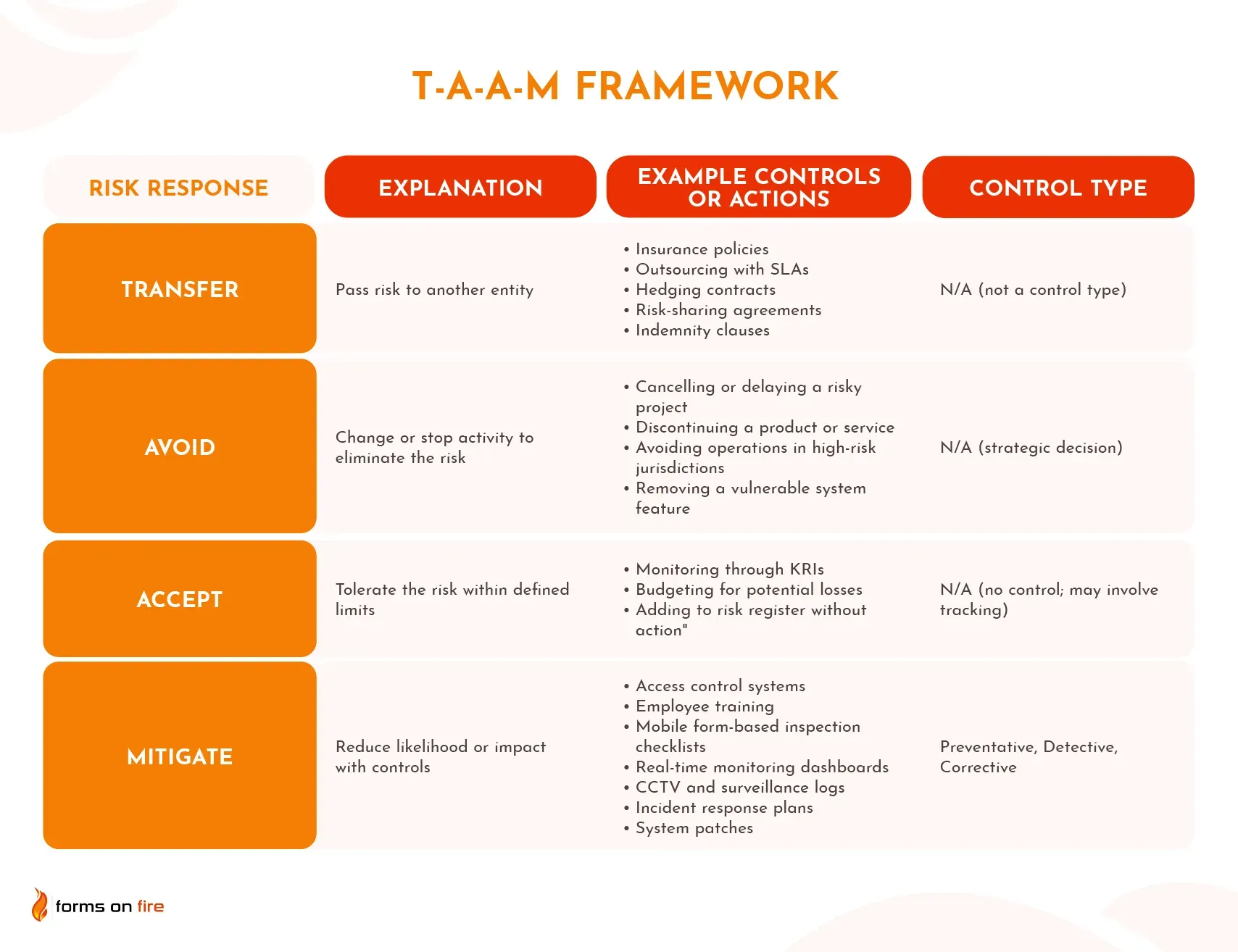
As with everything, technology has changed how organizations manage risk controls. Automation ensures consistent control execution without dependence on memory, while GRC platforms provide a single view of ownership and remediation progress.
TIP #1: Someone needs to own each control — without clear accountability, controls become ineffective fast.
TIP #2: Those controls need regular testing to prove they actually work, not just exist in a policy manual.
TIP #3: When resources are tight, prioritize based on what could hurt you most rather than spreading yourself too thin.
4. Monitoring and reporting
Continuous monitoring and reporting ensure that risks and controls remain within acceptable limits while keeping leadership informed of the organization's risk stance. This ongoing vigilance catches issues before they become crises and provides the transparency stakeholders need to make informed decisions.
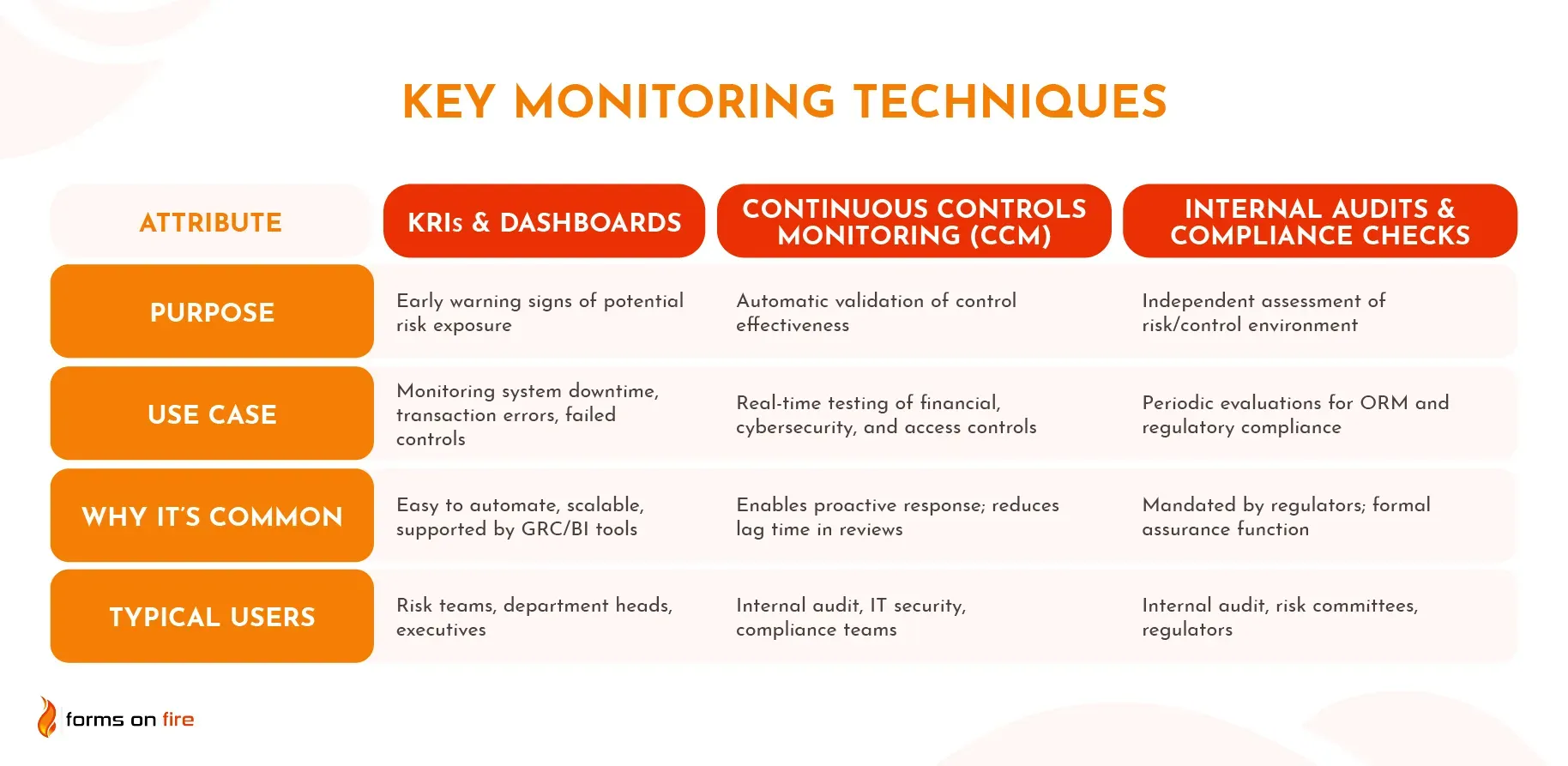
Key monitoring techniques include:
- Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) and dashboards: Real-time metrics that track early warning signs of emerging risks, displayed through visual dashboards for quick assessment.
- Continuous Controls Monitoring (CCM): Automated systems that constantly verify control effectiveness and immediately flag exceptions or failures.
- Internal audits and compliance checks: Periodic reviews that validate monitoring systems and assess overall risk management effectiveness.
Organizations face both internal and external reporting requirements that demand different approaches. Internal stakeholders — boards, C-suite executives, and risk committees — need strategic risk summaries focused on business impact and decision-making. External parties like regulators and auditors require detailed compliance documentation and standardized reporting formats.
The key is customizing each report to its target audience: board members may want high-level risk heat maps and trend analysis, while operations teams may need granular control of performance data and detailed exception information.
Tip #1: Clear escalation protocols form the backbone of effective monitoring programs. Everyone needs to know exactly when to escalate issues, who to contact, and what information to provide, ensuring critical risks reach decision makers quickly while avoiding unnecessary noise from routine matters.
How technology streamlines ORM
Modern technology transforms operational risk management from a reactive, spreadsheet-based exercise into a proactive, integrated system. Tools such as AI, workflow automation, GRC systems, and digital forms help organizations streamline their processes, improve data accuracy, and respond to risk in real time.
1. Automation of risk assessments and reporting
Digital platforms can automate how risks are identified, evaluated, and communicated across the organization. Risk scoring, trend tracking, and dashboard generation can all be automated based on predefined rules.
Where mobile forms shine: They allow frontline staff to perform inspections, conduct audits, submit incident reports, and provide other structured risk assessment data instantly from the field. This ensures real-time visibility and consistent documentation, especially in distributed or high-compliance environments.
2. Centralized risk data management
Technologies like cloud-based GRC platforms centralize data, enabling teams to break down silos and maintain a unified risk register across business units.
Again, mobile forms contribute by feeding structured data directly into these systems — including incident report forms, audit logs, and safety checklists — from remote or offline locations. This ensures that risk data isn't trapped in emails, paper, or inaccessible systems.
3. Real-time monitoring with AI and machine learning
AI and ML models can analyze large volumes of operational data to detect anomalies, forecast risk patterns, and alert managers to emerging threats.
This process is only as strong as the data that feeds it. Digital forms play a role here by enabling structured, high-quality frontline data capture — a key prerequisite for effective AI-driven analysis, especially in industries like construction, manufacturing, and logistics.
4. Scenario modelling and predictive analytics
Advanced tools can simulate the financial or operational impact of various risk events (e.g., cyberattack, supply chain disruption), helping leadership test their preparedness and prioritize controls.
Mobile data improves these models by providing granular inputs from the field — such as frequency of safety incidents or maintenance delays — which enhances the accuracy of predictive outcomes.
5. Regulatory compliance automation
RegTech tools and GRC platforms can automatically map evolving regulatory requirements to internal controls and trigger workflows to ensure compliance.
Mobile forms support this by enabling standardized audits and inspections that align with regulatory frameworks — whether OSHA, ISO, or industry-specific mandates. Digitized checklists, signatures, and timestamps create a reliable audit trail.
6. Incident management and response
Incident management systems log, escalate, and track events such as equipment failures, near-misses, or data breaches. These systems often integrate with workflow tools, notifications, and reporting dashboards.
Mobile forms accelerate this process at the point of origin. Field teams can document incidents immediately — including photos, GPS, and notes — triggering automated escalation paths and reducing response time.
Simplify risk management with Forms On Fire
Forms On Fire transforms how organizations capture, process, and act on field data. Instead of juggling paper forms, spreadsheets, and disconnected systems, you get a unified solution that turns any mobile device into a powerful data collection tool.
Here's how Forms On Fire streamlines your operational risk management:
- Risk identification: Frontline teams submit incident reports, safety observations, and risk assessments in real time, with photos, GPS, and timestamps.
- Risk assessment: Standardized digital forms ensure consistent data collection, and automated scoring eliminates manual errors.
- Mitigation: Digitize checklists, audits, and inspections with workflows that auto-assign issues to the right people.
- Monitoring: Real-time data feeds dashboards and alerts for instant visibility into emerging risks.
The result? Your operational risk management transforms from a reactive paper chase into a proactive, data-driven system that actually helps you prevent problems before they become crises.
Ready to see how Forms On Fire can revolutionize your risk management approach?
Schedule a demo today and
tell us what you're trying to accomplish
— we'll show you how Forms On Fire can help.




